A Beginner’s Guide to RFID Label Printing
30th Dec 2025
Technology continues to redefine how businesses track, identify, and manage assets. From retail shelves to shipping warehouses, RFID label printing has become one of the most efficient ways to streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve visibility across the supply chain. Unlike barcodes—which require a direct line of sight—RFID tags transmit data wirelessly, allowing hundreds of items to be scanned simultaneously.
At DuraFast Label Company, we’ve seen RFID evolve from a niche innovation into an essential business tool. More companies are recognizing that automating inventory control and data capture leads to faster, more accurate processes. Whether you’re a logistics manager tracking pallets or a retailer monitoring stock levels in real time, RFID technology helps bridge the gap between physical products and digital systems.
For businesses in search of reliable solutions, investing in RFID label printers in Canada can deliver measurable efficiency gains and long-term value. These printers not only encode data onto smart labels but also produce clear, durable printouts for barcodes, branding, and compliance information—all in one step.
What Is RFID Label Printing?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Each tag contains a microchip and antenna, enabling it to store and transmit data to a reader device. Unlike traditional barcodes, which require visual scanning, RFID labels can be read remotely—even when they’re hidden behind packaging, stacked in boxes, or located several feet away.
RFID Components Simplified
An RFID labeling system typically includes three components:
- Tags or Labels – These contain the embedded microchip and antenna that hold data such as item number, batch, or location.
- Readers – Devices that emit radio waves to detect and communicate with tags.
- Printers/Encoders – Machines that both print and encode the data onto the label surface.
When combined, these components create an intelligent labeling ecosystem capable of tracking assets automatically and accurately throughout their lifecycle.
Why RFID Is More Than Just a Label
The difference between a barcode and an RFID tag is like comparing a snapshot to a live feed. Barcodes provide static information printed on a surface. RFID tags, on the other hand, carry dynamic data that can be updated or rewritten as needed. They also transmit data without human intervention, meaning no manual scanning is required—saving time and reducing errors dramatically.
As a result, RFID technology is rapidly replacing traditional barcode systems in industries where speed, precision, and traceability are critical.
How RFID Label Printers Work
An RFID printer does more than apply ink to paper—it encodes electronic data into a smart label while printing the visual elements you see on the surface. This combination of digital and physical identification creates a single, powerful label capable of both visual and electronic tracking.
Here’s how the process works:
- Encoding the Chip
Each RFID label contains a small inlay with a chip and antenna. When the label passes through the printer, a built-in encoder writes unique data (such as serial number, product ID, or batch information) directly onto the chip. This information can later be read or updated by RFID scanners. - Printing the Label Surface
At the same time, the printer produces high-quality, human-readable text, graphics, and barcodes on the face of the label. This ensures that even if an RFID reader isn’t available, the label can still be identified visually or with a standard barcode scanner. - Verification and Error Checking
Advanced RFID printers verify that each tag was encoded successfully. If the printer detects an error or faulty inlay, it flags the label automatically—ensuring only functional tags are used. This feature prevents wasted media and guarantees accuracy. - Output and Application
Once printed, RFID labels can be automatically dispensed, rewound into rolls, or applied directly onto products, cartons, or pallets.
This all-in-one process minimizes manual steps and ensures every label leaving the printer is both readable and ready for automated tracking.
Types of RFID Label Printers
Just like traditional label printers, RFID models come in different categories depending on your application and print volume.
1. Desktop RFID Printers
Compact and efficient, desktop printers are ideal for low- to medium-volume operations like small retail stores, healthcare facilities, or libraries. They’re perfect for encoding tags on individual items, documents, or samples.
A great example is the SATO CT4-LX HF RFID Thermal Transfer Desktop Printer. This printer offers intuitive touch-screen control and automatic encoding verification, ensuring accurate tag production with minimal operator input. It’s compact enough for office use yet powerful enough for enterprise-level labeling.
2. Industrial RFID Printers
Built for speed and durability, industrial printers handle large-scale production environments such as manufacturing, logistics, and distribution centers. They’re designed for continuous operation, often running 24/7, and can manage thousands of encoded labels daily.
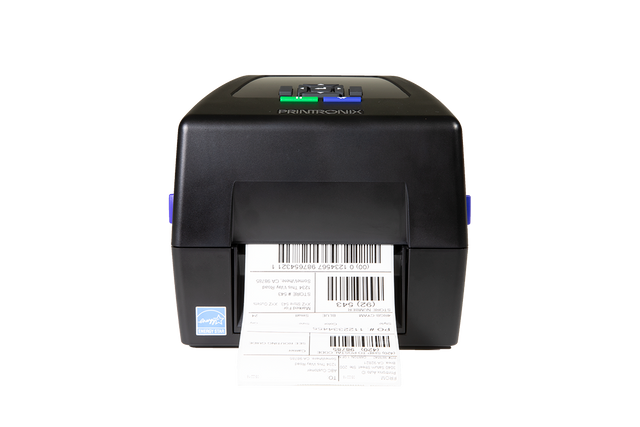
One of the most popular models is the Printronix T800 UHF RFID Thermal Transfer Label Printer. Known for its precision encoding and 300 DPI resolution, it’s compatible with a wide range of label materials and sizes. Businesses use it for retail compliance labeling, asset management, and pallet tagging—especially when working with retailers like Walmart and Nordstrom, who require RFID labeling compliance.
3. Specialized and High-Performance Models
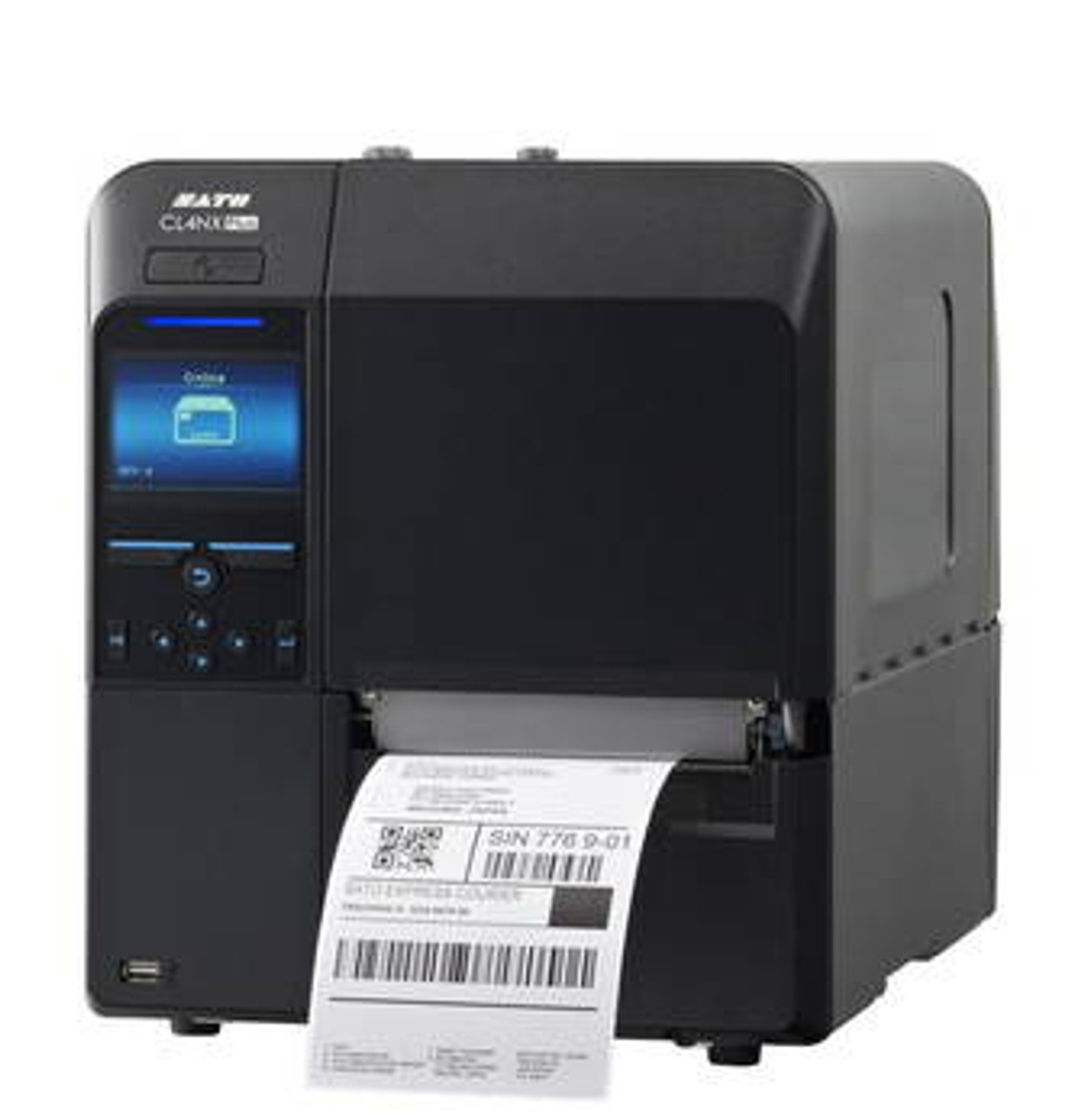
For businesses that need advanced tagging capabilities, high-performance RFID printers like the SATO CL4NX Plus UHF RFID Industrial Printer deliver exceptional speed, accuracy, and flexibility. This model supports a wide variety of RFID tags and encoding standards, making it suitable for complex supply chain and manufacturing environments.
Another notable option is the Printronix T800 RFID Jewelry Tag Printer, engineered for small, delicate labels often used in jewelry or electronics. It offers pinpoint accuracy when encoding miniature RFID tags, ensuring flawless readability across high-value inventory.
RFID Label Materials and Construction
Not all labels are created equal—especially when it comes to RFID. The performance of an RFID tag depends on the label’s material, adhesive, and the placement of the inlay.
RFID labels typically consist of several layers:
- Face Material: The printable surface, made of paper or synthetic film (such as polypropylene or polyester).
- Antenna and Chip: The electronic inlay that stores and transmits data.
- Adhesive Layer: Bonds the label securely to various surfaces—whether cardboard boxes, metal containers, or plastic packaging.
- Liner: The backing paper that supports the label during printing and application.
For durable applications, synthetic materials are preferred due to their resistance to moisture, heat, and abrasion. DuraFast Label Company supplies a variety of RFID-compatible materials engineered for consistent print performance and strong signal transmission.
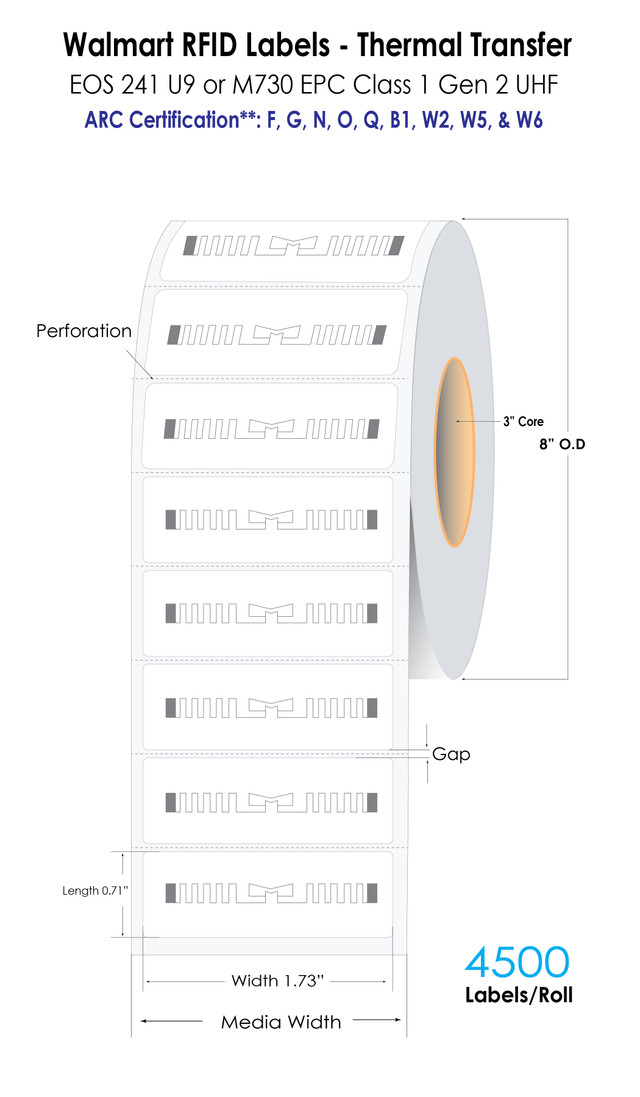
For large-scale retail compliance, many companies use Walmart RFID Labels (1.73" x 0.71"), which meet the retailer’s exact specifications. These labels combine excellent encoding reliability with high-quality printing, ensuring each product is traceable throughout its journey from warehouse to store.
Why Businesses Are Moving Toward RFID Labeling

RFID technology’s biggest advantage is automation. It eliminates the need for manual scanning and drastically reduces human error. Imagine scanning hundreds of boxes simultaneously as they move through a conveyor—without even touching them. That’s the level of efficiency RFID offers.
Other key advantages include:
- Inventory Accuracy: Near-100% tracking precision means fewer stock discrepancies.
- Speed: Instant bulk scanning improves receiving, picking, and shipping workflows.
- Data Visibility: Real-time insights into product movement and location.
- Security: RFID tags help prevent theft and counterfeiting by providing unique, trackable IDs.
At DuraFast Label Company, we help businesses design complete RFID printing systems that combine reliability and scalability. From printers and ribbons to software and tag media, every component is optimized to deliver seamless integration and long-term value.
Industries Benefiting from RFID Label Printing
While RFID labeling started as a niche technology in logistics and warehousing, it has now expanded into nearly every sector that values visibility, traceability, and automation. The ability to identify items wirelessly and in real time gives organizations a significant advantage in efficiency and accuracy.
At DuraFast Label Company, we’ve seen businesses across multiple industries transform their operations through RFID integration. Here are some of the most common sectors benefiting from this smart labeling solution.
1. Retail
Retailers are among the biggest adopters of RFID labeling technology. Major brands like Walmart and Nordstrom now require suppliers to tag products with RFID labels to streamline inventory and prevent stockouts.
By using smart tags instead of barcodes, retailers can scan entire pallets or racks of merchandise instantly—saving hours of manual labor each week.
RFID also enhances customer experience. It enables faster checkouts, supports “smart fitting rooms,” and provides accurate product availability online. The Printronix T800 UHF RFID Thermal Transfer Label Printer is particularly popular among retail suppliers because of its compliance with leading retailer RFID standards.
2. Logistics and Warehousing
In logistics, real-time visibility is everything. RFID labels make it possible to track shipments at every stage—from manufacturing to delivery—without manual scanning. This automation reduces bottlenecks and ensures the right packages reach the right destination on time.
Warehouses equipped with RFID readers can instantly identify inbound and outbound goods, monitor inventory levels, and even trigger alerts when items move incorrectly. Combined with automated conveyor systems, RFID helps achieve near-perfect accuracy rates while reducing human intervention.
3. Manufacturing and Automotive
Manufacturers use RFID to manage parts, track assemblies, and prevent production errors. Each component can be tagged with a unique identifier that follows it through the production line. If a part is installed incorrectly, the system immediately flags the issue, preventing costly mistakes.
In the automotive industry, RFID labels can withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions, ensuring parts are traceable throughout production and maintenance cycles.
4. Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Hospitals and pharmaceutical companies use RFID labels to improve patient safety and ensure compliance. Medications, surgical tools, and laboratory samples are tagged for precise tracking. RFID also helps monitor expiration dates and reduce inventory waste.
The SATO CL4NX Plus UHF RFID Industrial Printer is often used in these environments for its high accuracy and secure data encoding, ensuring medical labeling meets strict regulatory standards.
5. Jewelry and Luxury Goods
RFID has become the gold standard for tracking high-value items. Jewelers and luxury brands use compact, specialized tags to monitor inventory and authenticate products.
The Printronix T800 RFID Jewelry Tag Printer delivers precise, high-resolution printing for small, detailed tags—perfect for labeling items like rings, watches, and electronics. These labels provide both visual and digital identification, protecting brands against loss and counterfeiting.
6. Public Sector and Libraries
Even public institutions are benefiting from RFID. Libraries use it to track books, manage lending systems, and improve user convenience. Government facilities employ RFID tags to secure equipment and manage access control.
Across all industries, the message is clear: RFID label printing enables smarter operations, better accountability, and higher productivity.
Setting Up Your RFID Printing System
Implementing RFID technology isn’t just about buying the right printer—it’s about creating a complete ecosystem that connects hardware, software, and materials. Here’s how to set up an efficient and reliable RFID label printing workflow.
1. Choose the Right Printer for Your Needs
Start by assessing your volume, label size, and application environment.
For smaller operations or offices, desktop models like the SATO CT4-LX HF RFID Printer offer compact versatility. For high-throughput industrial use, larger models such as the SATO CL4NX Plus UHF RFID Industrial Printer or high-quality thermal label printers are better suited for durability and scalability.
Each printer supports specific RFID tag frequencies and encoding standards, so compatibility with your reader system is crucial.
2. Use RFID-Compatible Labels and Ribbons
The label material directly affects encoding performance. Metallic surfaces or thick materials can interfere with radio waves, so choose RFID labels specifically designed for your products and packaging.
DuraFast Label Company supplies RFID labels that meet industry standards such as Walmart’s compliance format. These labels are engineered for reliable signal transmission while maintaining exceptional print quality.
Pair your labels with custom thermal transfer labels for optimal results—especially when long-term durability is required.
3. Integrate with Software
Your printer needs to communicate with your inventory or ERP system. Label design software—such as Bartender or NiceLabel—helps manage templates, encode data, and generate accurate print runs. Integration ensures every tag receives the correct information, eliminating duplication or data mismatches.
4. Calibrate and Test
Before starting full production, calibrate your printer. This process ensures the encoder aligns with the RFID inlay and verifies successful data transmission.
Most modern printers have built-in diagnostic tools that check tag readability automatically. Run a small test batch to confirm that each encoded tag is being detected by your readers.
5. Train Your Team
Even with user-friendly equipment, training operators is key. Teach staff how to replace rolls, verify tags, and troubleshoot issues. A well-trained team reduces downtime and maintains production quality.
By following these steps, your RFID system will run smoothly, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and compliance across every labeling operation.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them

While RFID labeling offers many benefits, improper setup or material selection can cause issues. Here are the most common challenges businesses face—and how to resolve them.
1. Tag Read Failures
One of the most frequent problems is unreadable tags. This can result from poor label placement, incompatible materials, or incorrect encoding.
To avoid this, use high-quality tags from reputable suppliers and ensure proper alignment during printing. Testing different label positions on your product can help you identify optimal read zones.
2. Interference from Surfaces
Metallic or liquid-filled products often block radio signals. To overcome this, use on-metal RFID tags or add a small foam spacer between the tag and surface. Specialized labels designed for these environments ensure consistent read performance.
3. Printer Calibration Issues
If tags are not being encoded correctly, recalibrate your printer’s sensor alignment. Verify the inlay position and use the printer’s verification feature to identify defective tags before application.
Models like the Printronix T800 UHF RFID Printer include automatic tag detection, reducing manual calibration needs.
4. Material or Ribbon Incompatibility
When labels smudge or fade quickly, it usually indicates a mismatch between ribbon and substrate. Resin ribbons work best with synthetic materials such as polyester or vinyl, while wax/resin blends suit coated papers. Consulting your supplier—like DuraFast—ensures you get the right combination.
5. Environmental Conditions
Temperature, humidity, and chemicals can impact adhesive strength and readability. For harsh conditions, use durable, weather-resistant materials. Pairing weatherproof labels with resin-based printing ensures long-lasting performance even outdoors or in cold storage.
6. System Integration Errors
Sometimes, tags are encoded correctly, but the data doesn’t sync with backend systems. This usually occurs due to integration errors or network issues. Proper software configuration and data mapping prevent mismatches between printed labels and your database.
RFID Labeling Best Practices
Beyond troubleshooting, there are a few industry-proven best practices to maintain consistent results:
- Keep Supplies Consistent: Stick to one brand of RFID labels and ribbons to ensure repeatable performance.
- Monitor Quality: Conduct regular tag verification tests to detect defective batches early.
- Label Placement: Always apply tags flat and free from wrinkles or air bubbles to prevent misreads.
- Update Firmware: Regularly update your printer’s firmware to stay compatible with new tag standards.
- Work with Experts: Partnering with a supplier like DuraFast Label Company ensures you have access to technical support and reliable materials that meet your workflow’s demands.
Adhering to these practices minimizes waste and maximizes the lifespan of your RFID equipment and tags.
The Future of RFID Label Printing
RFID technology is evolving rapidly, reshaping how businesses collect and process information across entire ecosystems. The combination of smart labeling, automation, and cloud connectivity is creating what many experts call the “intelligent supply chain.” Companies are no longer limited to static data—they now have live visibility into how goods move, where they are, and what condition they’re in.
Over the next decade, RFID adoption will expand even further as costs continue to drop and performance improves. Here’s how the next phase of innovation is taking shape.
1. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things)
RFID is at the heart of the Internet of Things. When products are tagged with RFID and connected to sensors, they become part of a dynamic data network. Every item can “talk” to the system—reporting its status, temperature, or location automatically.
In logistics, this enables predictive analytics: shipments can be rerouted before delays occur. In manufacturing, real-time monitoring ensures no component goes missing in assembly lines. RFID labels, when paired with IoT devices, unlock an unprecedented level of operational intelligence.
2. Sustainability and Recyclable Tag Materials
As environmental awareness grows, RFID manufacturers are developing eco-friendly tags using paper-based antennas and biodegradable adhesives. These innovations help businesses comply with sustainability mandates while maintaining performance.
At DuraFast Label Company, sustainability is an ongoing focus. We work with suppliers who are pioneering recyclable tag materials and solvent-free adhesives to ensure labeling systems are both efficient and environmentally responsible.
3. Miniaturized and Flexible RFID Tags
New generations of RFID chips are smaller, thinner, and more adaptable than ever. Flexible inlays can now be embedded into textiles, medical supplies, and even packaging film without compromising performance. These ultra-light tags open doors for creative labeling applications in apparel, food safety, and healthcare.
4. Blockchain and RFID Integration
Combining blockchain with RFID creates a tamper-proof record of every item’s journey from production to delivery. For high-value goods such as luxury accessories or pharmaceuticals, this means every tag’s data—location, authenticity, and condition—can be verified instantly through a blockchain ledger. This innovation ensures trust and transparency across the entire value chain.
5. Automation in Label Production
Modern RFID printers, such as the SATO CL4NX Plus UHF RFID Industrial Printer, are equipped with automated encoding and error-detection features that minimize waste and boost production speed. Automation in both printing and application ensures consistent tag quality across large batches.
The future of RFID printing lies in convergence—where smart labels, analytics, and automation merge into a seamless system. Businesses that adopt these technologies early position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly data-driven world.
RFID and Data Security
While RFID brings enormous advantages, it also raises questions about data privacy and protection. Tags contain unique identifiers that can be read remotely, which means businesses must implement proper security protocols to prevent unauthorized access.
To safeguard sensitive data:
- Use encrypted RFID tags and readers that require secure authentication.
- Employ frequency-specific shielding to prevent external reads.
- Ensure that encoded information complies with privacy regulations like GDPR.
Leading RFID printers now include built-in security features that allow selective data encryption, making the technology safer for high-security applications such as healthcare or financial asset tracking.
DuraFast Label Company helps clients configure these safeguards properly, ensuring compliance without compromising efficiency.
Why Choose DuraFast Label Company for RFID Label Printing
Choosing the right RFID system can be complex, but partnering with an experienced provider simplifies the journey. At DuraFast Label Company, we guide businesses from setup to scaling—ensuring every piece of hardware, software, and consumables works together perfectly.
Our range includes industry-leading printers like:
- The Printronix T800 UHF RFID Printer ideal for logistics and retail compliance.
- The SATO CT4-LX HF RFID Printer for compact office or lab use.
- Specialized Walmart RFID Labels that meet strict global compliance requirements.
But hardware is only part of the solution. We also provide technical training, custom label recommendations, and ongoing support to ensure your RFID system delivers consistent, accurate performance.
Common Misconceptions About RFID Printing
Despite its widespread success, some myths about RFID labeling still persist. Let’s debunk the most common ones:
“RFID is too expensive.”
While RFID systems used to be costly, advancements in technology have drastically reduced costs. Today, RFID printing is accessible to small and medium-sized businesses, not just large corporations. The return on investment comes from automation and reduced errors.
“Barcodes are enough for inventory management.”
Barcodes serve well in basic tracking, but they can’t compete with RFID’s real-time, multi-item scanning. RFID improves operational efficiency and visibility, which is critical in fast-moving industries.
“RFID tags only work on certain materials.”
While metals and liquids can interfere with signals, modern RFID tags are available in on-metal and specialty formats that perform well even on challenging surfaces.
These misconceptions often hold businesses back from upgrading to a more efficient, intelligent labeling system. Working with an expert partner ensures you implement the right RFID solution for your specific needs.
Emerging Use Cases: Beyond Tracking
As RFID technology matures, businesses are discovering creative applications beyond basic tracking. For example:
- Event Management: Wristbands with embedded RFID chips simplify access control and payment systems.
- Waste Management: Smart bins tagged with RFID allow municipalities to track recycling performance.
- Food and Agriculture: RFID sensors can record temperature data for perishable goods, improving safety and reducing spoilage.
These innovations illustrate how RFID is no longer limited to warehouses—it’s becoming an integral part of everyday life.
How RFID Enhances Business Intelligence
The data generated from RFID systems fuels deeper business insights. When integrated with analytics platforms, RFID tracking data helps identify process inefficiencies, forecast demand, and optimize workflows.
Imagine a distribution center knowing not just where inventory is, but how long it stays in each zone or when it’s most likely to move. That kind of intelligence helps businesses fine-tune operations, reduce waste, and increase customer satisfaction.
When paired with high-quality thermal label printers, RFID systems deliver not just operational efficiency, but also actionable insights that strengthen decision-making.
Your Path to Smarter Labeling Starts Here

RFID labeling isn’t just a technical upgrade—it’s a strategic investment in efficiency, visibility, and growth. As automation becomes the norm, companies that embrace RFID today will set the standard for the future of logistics, retail, and manufacturing.
At DuraFast Label Company, we’re proud to be at the forefront of this transformation. From RFID label printers in Canada to encoding supplies and tag media, we provide everything businesses need to build reliable, scalable, and intelligent labeling systems.
Our experts assist in selecting the right printers, integrating label software, and supplying compliant RFID tags like Walmart RFID Labels for global retailers.
If your goal is to improve traceability, speed, and accuracy, our combination of custom thermal transfer labels, high-quality thermal label printers, and RFID label printers in Canada provides a complete, future-ready solution.
To learn more about setting up or upgrading your RFID labeling system, contact our team today. Our specialists are ready to help you design an RFID workflow that meets your unique operational needs—efficiently, affordably, and intelligently.